- Department of Civil Engineering and Urban Design
- Department of Architecture
- Department of Mechanical Engineering
- Department of Electrical and Electronic Systems Engineering
- Department of Electronics and Information Systems Engineering
- Department of Applied Chemistry
- Department of Environmental Engineering
- Department of Biomedical Engineering
- Department of General Education
- Division of Human Sciences
- Center for Monodzukuri Management
- Monodzukuri Center (MONOLAB.)
- Nanomaterials Microdevices Research Center
- Research Center for Environmental Bioresource
- Robotics & Design Center
- Xport
- Digital Archives Center
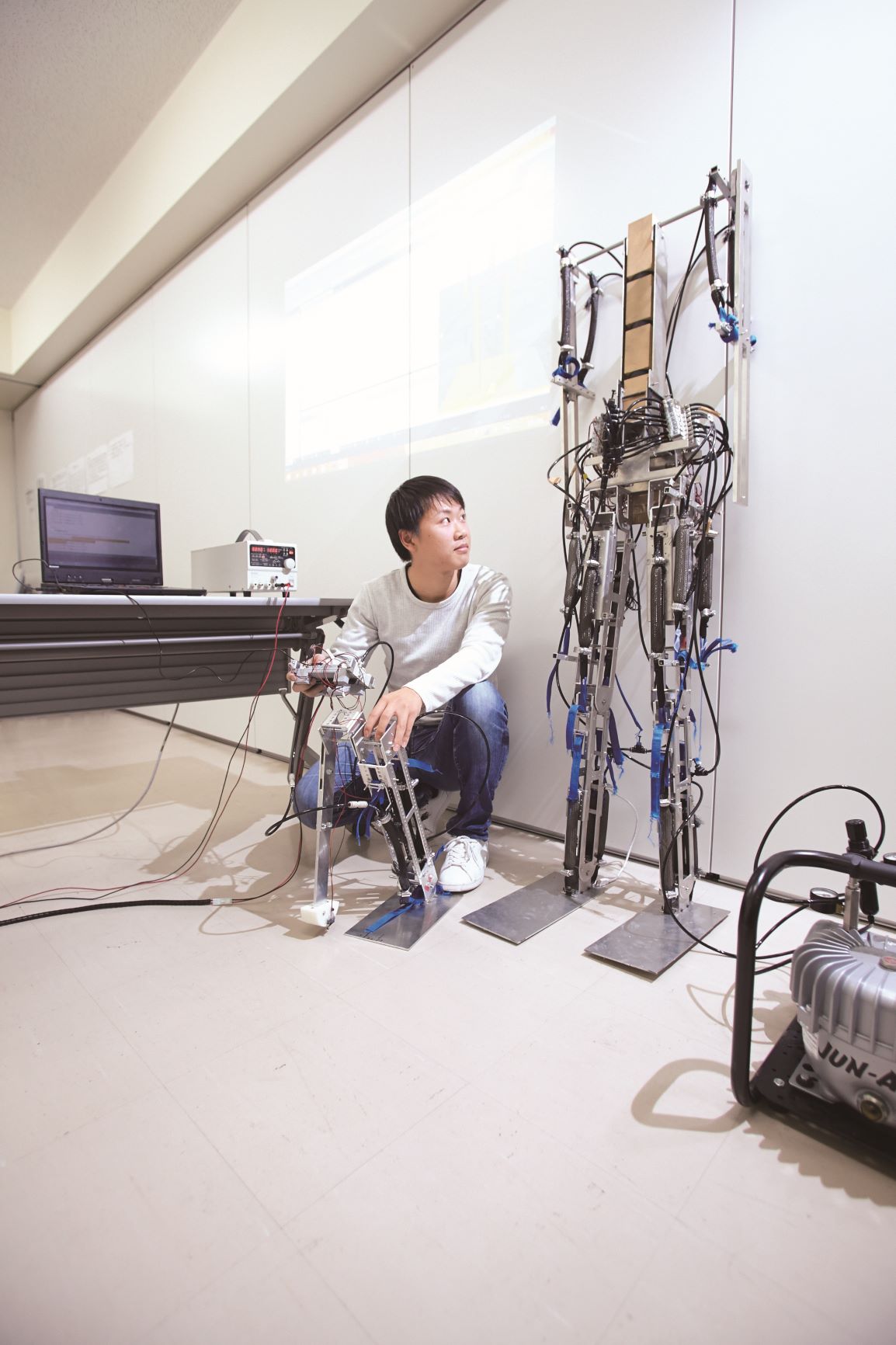
- Human Robotics R&D Center
- Virtual Reality Laboratory
- Visualization Software Developing Center
- Yawata Engineering Laboratory
- Incubation Lab
Researchers in Graduate School and Faculty of Engineering (AY2024)
Department of Civil Engineering and Urban Design
Department of Civil Engineering and Urban Design
-

10,000kN Vertical Loading Equipment, Structure Research Center
-
Urban Design and Simulation
The Civil Engineering and Urban Design program offers an efficient, high-level curriculum based on an original educational philosophy, and includes courses that prepare students to obtain professional licenses. Students are given consistent guidance not only to help them graduate, but also to find work in their chosen fields. Students in the program study one fundamental area, design and planning, and five specialties: "Design and Planning," "Structures," "Materials," "Geotechnical Engineering," and "Hydraulic Engineering." In contemporary practice, maintaining, and preserving existing infrastructure is just as important as developing new projects. Engineers and designers must be able use a global perspective and fully understand the circumstances surrounding their projects. Students in our program systematically study how to solve difficult problems that affect urban spaces and develop their capacity to competently practice Civil Engineering and Urban Design.
Graduate Course in Civil Engineering and Urban Design
| Name (LAST NAME, First Name) * Click Name for Details |
Title | Research Field | Related Info. |
| INOUE, Susumu | P | Civil engineering materials/ Construction/ Construction management | Lab |
| TANAKA, Kazunari | P | Design science, Town planning/Architectural planning, Civil engineering project/Traffic engineering | Lab |
| OHYAMA, Osamu | P | Structural engineering/ Earthquake engineering/ Maintenance management engineering | Lab |
| MIKATA, Yasuhiro | P | Civil engineering materials/ Construction/ Construction management | Lab |
| HIOKI, Kazuaki | P※ | Geotechnical Engineering, Geotechnical Disaster Prevention | Lab |
| YAMAGUCHI, Yukikazu | P | Town Planning/ Transport Planning | Lab |
| AZUMA, Ryoukei | AP | Natural Disaster Science, Hydraulic engineering, Environmental Hydraulics | Lab |
| FUJIMOTO, Tetsuo | AP | Geotechnical engineering, Structural engineering/ Earthquake engineering/ Maintenance management engineering | Lab |
| IMAGAWA, Yusuke | AP | Structural engineering/ Earthquake engineering/ Maintenance management engineering | Lab |
| NISHIHORI, Yasuhide | AP | Infrastructure Planning and Management, Traffic Engineering/ City Planning | Lab |
| OGAWA, Yoshiya | AP | Hydraulic engineering | |
| KIMURA, Yusuke | AP | Civil engineering project/Traffic engineering, Town planning/Architectural planning |
Department of Architecture
Department of Architecture
-

Full size experiment of truss structure, Structure Research Cente
-

Critique of Students' Architectural Design
Graduate Course in Architecture
| Name (LAST NAME, First Name) * Click Name for Details |
Title | Research Field | Related Info. |
| TERAJI, Hiroyuki | P | Architectural Design, Design method | Lab |
| HONDA, Masaaki | P | Architectural history / Design | Lab |
| BABA, Nozomu | P※ | Building structures/ Materials | Lab |
| YOSHIDA, Tetsu | P | Architectural Planning, Social welfare and social work studies | Lab |
| NAKAMURA, Shigeharu | P | Building structures/ Materials | Lab |
| KONO, Ryohei | P | Architectural Environmental Engineering | Lab |
| OKAYAMA, Toshiya | P | Town planning, Architectural planning | Lab |
| MIZUSHIMA, Akane | P | Architectural history / Design, Town planning / Architectural planning | |
| LIN, Xiaoguang | AP | Building structures/ Materials | Lab |
| MUKAIDE, Seiji | AP | Building structures/ Materials | Lab |
| TAKINO, Atsuo | AP | Structural Engineering | Lab |
| QUAN, Chunri | AP | Seismic Engineering, Structural Engineering | Lab |
| FUJII, Shinsuke | AP | Architectural design | Web, Lab |
| NGUYEN, Thu Lan | ATP | ||
| IMAGAWA, Hikaru | RA | Building environmental engineering |
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Department of Mechanical Engineering
-
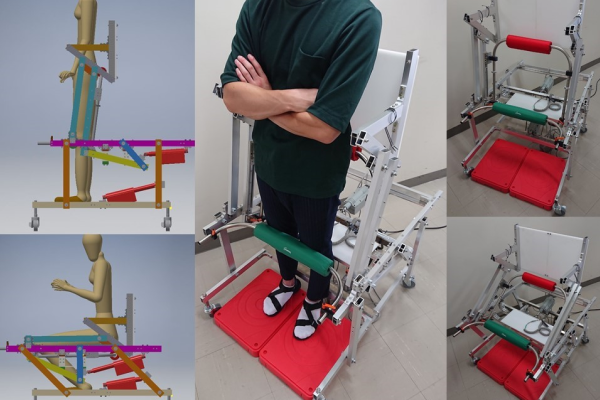

Standing-up motion rehabilitation device
-

Visualization of flow around automobile
Graduate Course in Mechanical Engineering
- Strength of Materials: Material Design, Functional Materials, Experimental Mechanics
- Machinery System Design and Production: Material Processing, Precision Engineering, Astronautics, Aeronautics, Automotive
- Heat Transfer and Fluid Mechanics: Heat Transport Phenomena, Mathematical Fluids, Turbomachinery, Internal Combustion Engines
- Measurement and Control Systems: Intelligent Systems and Control, Vibration, Sensing Technology, Robotics, Machine and Robot Systems
Master students belong to each field and may supplement their regular lectures with other lectures in mathematics, foreign languages, and other fields. Students will be chiefly involved in the research and development section in their chosen field.
| Name (LAST NAME, First Name) * Click Name for Details |
Title | Research Field | Related Info. |
| HAGA, Toshio | P | Casting / Roll Casting, Die casting | Web, Lab, Project |
| IHARA, Yukitoshi | P | Production engineering / Processing studies | Lab |
| KUWAHARA, Kazunari | P | Thermal engineering | Lab |
| UETSUJI, Yasutomo | P | Materials / Mechanics of materials | Lab |
| USHIDA, Shun | P | Control engineering / System engineering | Lab |
| MIYABE, Masahiro | P※ | Fluid engineering | Lab |
| YOSHIDA, Junji | P | Dynamics/Control | Lab |
| YAMAURA, Shinichi | P | Structural engineering/Earthquake engineering/Maintenance management engineering, Structural/Functional materials | Lab |
| NISHIKAWA, Izuru | P | Materials / Mechanics of materials | Lab |
| UEDA, Sei | P | Materials / Mechanics of materials | Lab |
| MATSUSHIMA Eiji | AP | Thermal engineering | Lab |
| HASHIMOTO, Tomoaki | AP | Control engineering / System engineering | Lab |
| IYOTA, Muneyoshi | AP | Materials/Mechanics of materials, Welding | Lab |
| UKAI, Takahiro | AP | Flow visualization, Compressible flow | Lab |
| HARAGUCHI, Makoto | AP | Rehabilitation science / Welfare engineering | Lab |
| YOKOYAMA, Sho | ATP | Biomedical engineering / Biomaterial science and engineering | Lab |
Department of Electrical and Electronic Systems Engineering
Department of Electrical and Electronic Systems Engineering

| Name (LAST NAME, First Name) * Click Name for Details |
Title | Research Field | Related Info. |
| KASE, Wataru | P | Dynamical system theory | Lab |
| MORIZANE, Toshimitsu | P★ | Power engineering / Power conversion / Electric machinery | Lab |
| MAEMOTO, Toshihiko | P | Semiconductor devces, New functional devices, Oxide semiconductors, Thin-film devices, Flexible devices | Lab |
| YOSHIMURA, Tsutomu | P | Integrated circuit design | Lab |
| SHIGEHIRO, Yuji | P | Mathematical informatics | Lab |
| MIICHI, Tomoaki | P※ | Power engineering / Power conversion / Electric machinery | Lab |
| TAKUMA, Takashi | P | Intelligent mechanics / Mechanical systems | Lab |
| FUJII, Akihiko | P | Electronic materials / Electric materials | Lab |
| YOSHIDA, Keiichiro | P | Environmental engineering and reduction of environmental burden, Plasma electronics, Energy engineering | Lab |
| SHINDO, Masako | AP | Plasma science | Lab |
| KOYAMA, Masatoshi | AP | Semiconductor engineering, Electron device/Electronic equipment, Physics of semiconductors | Lab |
| KANESHIRO, Yoshimori | AP | Electron device/Electronic equipment | Lab |
| MATAYOSHI, Hidehito | ATP | Power engineering / Power conversion / Electric machinery | Lab |
| JINNO, Souma | ATP | Power engineering / Power conversion / Electric machinery |
Department of Electronics and Information Systems Engineering
Department of Electronics and Information Systems Engineering

| Name (LAST NAME, First Name) * Click Name for Details |
Title | Research Field | Related Info. |
| HARASHIMA, Katsumi | P | Artificial Life / Multi-Agent | Lab |
| ZHOU, Hong | P | Communications, Wireless / Radio communications | |
| KOIKE, Kazuto | P | Electronic materials/ Electric materials | Lab |
| KAMIMURA, Tomosumi | P | Optical engineering, Photon science | Lab |
| OKU, Hiroshi | P※ | Control Engineering and Systems Science | Web Lab |
| KUMAMOTO, Kazuo | P | Communication / Network engineering | Lab |
| MATSUNO, Fumitoshi | P | Robotics, Mechatronics, Rescue Engineering | Lab |
| FUJIMURA, Masao | AP | Communication / Network engineering, Information network, Human interface and interaction, Multimedia database | Lab |
| HIROSHIBA, Nobuya | AP | Nano/Microsystems, Device related chemistry, Thin film/Surface and interfacial physical properties, Electronic materials/Electric materials | Lab |
| YASUKUNI, Ryohei | AP | Optical engineering, Photon science | Lab |
| KINJO, Ryouta | AP | Computer Simulation, AI, Superconducting Device | Lab |
| KAWAKAMI, Masashi | ATP | Communication / Network engineering, Electron device / Electronic equipment | Lab |
| TANIGAKI, Yuki | ATP | Lab | |
| WANG, Xixun | ATP | Intelligent mechanics / Mechanical systems |
P = Professor
AP = Associate Professor
ATP = Assistant Professor
※ = Department Chair
Department of Applied Chemistry
Department of Applied Chemistry
- Design of functional polymers and/or semiconductors at atomic, molecular, mesoscopic, and macroscopic levels
- Development of advanced chemical reaction processes based on "green sustainable chemistry"
- Synthesis of novel organic materials and their application to bioscience products and fine chemicals
| Field | Key words |
|---|---|
| Synthetic Chemistry | Electropolymerization, latent initiator, green catalyst |
| Organic Functional Chemistry | Host-guest chemistry, interlocked molecules, supramolecular chemistry, materials for energy conversion |
| Advanced Polymer Materials | Advanced functional polymers, polymer physics, composite materials, advanced particulate materials, soft dispersed systems |
| Inorganic Materials Chemistry | Nano materials, capacitor, plasmon sensor, photocatalyst, solar cell, ionic conductors, rechargeable battery |
| Molecular Recognition Chemistry | ISE, fluorescent probe, chemiluminescence, pulsed NMR |
| Materials and Life Chemistry | Green synthetic processes, surfactants, natural products, total synthesis |
The educational program is designed to develop students' thinking and technical skills that are appropriate for chemical engineers, researchers and other professionals in chemical industries and related areas. Academic staff with sophisticated expertise assist students in their learning of fundamental chemistry and experimental techniques. Students are encouraged to become familiar with international chemical journals and to make dynamic and persuasive presentations before professional audiences.

Graduate Course in Applied Chemistry
| Name (LAST NAME, First Name) * Click Name for Details |
Title | Research Field | Related Info. |
| MURAOKA, Masahiro | P | Organic Chemistry, Functional solid state chemistry | Web Lab |
| MORIUCHI, Takayo | P | Analytical Chemistry, Chemical Sensing | Lab |
| FUJII, Syuji | P | Polymer / Textile materials | Web Lab |
| HIGASHIMOTO, Shinya | P※ | Catalysis, Photoelectrochemistry | Lab |
| SHIMOMURA, Osamu | P | Polymer Synthesis, Hybrid Materials | Web Lab, Project |
| MASUYAMA, Araki | P | Organic Chemistry | Web Lab |
| NAKAMURA, Yoshinobu | P | Polymer chemistry | Web Lab |
| FUJIMORI, Keiichi | AP | Analitical Chemistry, Environmental Chemistry | Lab |
| OHTAKA, Atsushi | AP | Catalyst/Resource chemical process | Web Lab |
| KOBAYASHI, Shoji | AP | Synthetic organic chemistry | Web Lab |
| MURATA, Michihisa | AP | Organic chemistry/ Energy-related chemistry/ Device related chemistry/ Nanomaterials chemistry | Web Lab |
| HIRAI, Tomoyasu | AP | Polymer chemistry | Web Lab |
| HIRAHARA, Masanari | AP | Inorganic chemistry, Energy-related chemistry | Lab |
| MATSUMURA, Yoshimasa | ATP | Polymer chemistry | |
| FUKUSHIMA, Takashi | ATP | Inorganic chemistry, Energy-related chemistry, Green/Environmental chemistry |
Department of Environmental Engineering
Department of Environmental Engineering
Practical learning program directed toward real environmental affairs
Become governmental officers and environmental planners
Become front-line environmental engineers
Graduate Course in Environmental Engineering
From specialist to researcher
Environmental solutions
Coupling of education and research on current issues
| Name (LAST NAME, First Name) * Click Name for Details |
Title | Research Field | Related Info. |
| WATANABE, Nobuhisa | P | Civil and environmental engineering | Lab |
| KASAHARA, Shinsuke | P | Civil and environmental engineering / Design and evaluation of sustainable and environmental conscious system | Lab |
| KOSAKI, Yasunori | P※ | Civil and environmental engineering / Environmental engineering and reduction of environmental burden | Web, Lab |
| TAKAYAMA, Naru | P | Environmental agriculture (including landscape science) | Lab |
| KAWAMURA, Koji | AP | Aquatic life science, Conservation of biological resources, Horticultural science | Lab |
| HEGURI, Satoshi | AP | Condensed matter physics II | Lab |
| KUSAKABE, Taketoshi | AP | Environmental engineering, Aquatic environment, Waste & resource cycling | Lab |
| KAGATA, Kakeru | ATP | Thermal engineering | Lab |
| AWATA, Takanori | ATP | Environmental Engineering | Lab |
Department of Biomedical Engineering
Department of Biomedical Engineering

Biomedical engineering covers a multidisciplinary field that combines medicine, biology, agriculture, etc. in addition to engineering. There are full-time and specially appointed faculty members who have obtained a degree specializing in each field. We can conduct education and research in a wide range of fields such as life science, medical engineering, and food.
In addition to education and research on biomedical engineering, we are also focusing on manufacturing education based on the "environment and mind of manufacturing" cultivated in the long tradition of 100 years, which is the strength of Osaka Institute of Technology.
A unique "Rotational Laboratory Experimental Course," which is provided in all of the ten laboratories through three sequential semesters in sophomore and junior years, helps students master practical research skills from faculties who have a broad spectrum of biomedical engineering research experience. These programs provide students with knowledge and skills in applied life sciences, and the solid background in engineering that they need to pursue graduate school studies, or careers in the medical, healthcare, and food industries.
We are also focusing on employment guidance and graduate school admission guidance that make use of these.
Graduate Course in Biomedical Engineering
| Name (LAST NAME, First Name) * Click Name for Details |
Title | Research Field | Related Info. |
| FUJISATO, Toshiya | P※ | Biomedical engineering / Biomaterial science and engineering | Lab, Project |
| ASHITAKA, Emiko | P | Neurochemistry / Neuropharmacology, Molecular biology, Pathological medical chemistry | Lab, Project |
| KAWAHARA, Ko-ichi | P | Lifestyle-related inflammatory diseases, Food science | Lab |
| UTO, Sadahito | P | Bioerectronics | Lab |
| NAGAMORI, Eiji | P | Biochemical Engineering | Lab |
| MATSUMURA, Kiyoshi | P | Physiology | Lab |
| TONAMI, Hiroyuki | AP | Biomedical engineering / Macromolecular chemistry | Lab |
| OHMORI, Taketo | AP | Applied microbiology, Enzyme engineering | Lab |
| SAKIYAMA, Ryoichi | AP | Biomedical engineering / Biomaterial science and engineering, Biofunction / Bioprocess | Lab |
| FUJITA, Hidetoshi | AP | Laboratory animal science, Pathological medical chemistry, Molecular biology | Lab |
Department of General Education
Department of General Education
| Name (LAST NAME, First Name) * Click Name for Details |
Title | Research Field | Related Info. |
| HAYASHI, Masahito | P | Science education, Elementary Particle Physics | |
| TANAKA, Jun | P | Geology | |
| ISHIKAWA, Tsuneo | P | Algebra | |
| HARADA, Yoshiyuki | P | Condensed matter physics I, Nanomaterials engineering | |
| TSUKAMOTO, Tatsuya | P | Geometry | Web |
| TANI, Yasutaka | P※ | Geology | |
| FUJIMOTO, Akira | P | Condensed matter physics I | Lab |
| MYO, Takayuki | P | Nuclear Physics | |
| HATTORI, Tetsuya | AP | Spectral Theory for Operators | |
| SHIRAI, Shinichi | AP | Basic analysis | Web |
| MITSUHASHI, Masako | AP | Biodiversity / Systematics | |
| KISHIMOTO, Kengo | AP | Geometry | Web |
| HASEGAWA, Takayuki | ATP | Nanostructural physics/ Condensed matter physics I | Web, Lab |
| NOZAWA, Masato | ATP | Gravitational Physics | Web, |
| MONNAI, Akihiko | ATP | Nuclear Theory | Web, |
| SATO, Yusuke | ATP | ||
| KUMASHIRO, Shinya | ATP | Algebra | |
| MATSUZAKI, Ryo | ATP |
Division of Human Sciences
Broaden your horizons, train your body, and study a wide variety of academic subjects to enrich your education and have a sound judgement of things
Curriculum
| Fields | Subjects |
|---|---|
| Social Sciences and Humanities | Introduction to the Humanities Basic Writing Skills Philosophy Ethics History of Art Literature History of Japanese Language Jurisprudence (the Constitution of Japan) Economics History Psychology Japanese Tradition and Culture International Relations Japanese Culture and Society I/II* |
| Languages | Basic English a/b Oral Communication Ia/Ib/IIa/IIb Basic English for Technical Communication a/b Career English Ia/Ib/IIa/IIb English Presentation a/b Chinese Communication Chinese and Contemporary Chinese Studies Study Abroad Japanese I/II* |
| Physical Education | Health-Related Physical Education I/II Lifelong Sports I/II |
| Name (LAST NAME, First Name) * Click Name for Details |
Title | Research Field | Related Info. |
| MUKUHIRA, Atsushi | P | British and American theater, ESP, Cultural policy and management | |
| KAWATA, Susumu | P | Sociology / Area studies | |
| TSUJIMOTO, Tomoko | P | English linguistics | |
| KAMIKUBO, Satoshi | P | History of Japanese Economic Thought | |
| MATSUURA, Kiyoshi | P | Fine art history, Cultural assets study and museology | |
| UCHIDA, Hiroaki | P※ | Philosophy / Ethics | |
| NAKAMURA, Tomohiro | P | Sports science | Lab, Project |
| OTANI, Mayumi | P | Clinical psychology | |
| YONEDA, Tatsuro | P | Japanese linguistics | |
| NISHIWAKI, Masato | AP | Sports Science, Applied Health Science, Physical Education | Lab |
| ISHIDO, Minenori | AP | Sports science, Cognitive science | Lab |
| OTSUKA, Seiko | ATP | Socilinguistics, Gender Studies / Linguistics | |
| TAKIKAWA, Hiroki | ATP | Literature in English | |
| NISHIYAMA, Yurika | ATP | Japanese history, Politics | Lab |
| ODA, Tomoko | ATP | Literature in English | |
| TACHIBANA, Misato | RA | Sports science, English linguistics |
Center for Monodzukuri Management
-
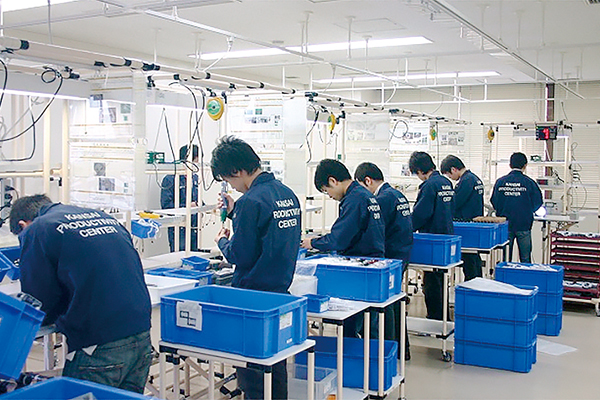

Exercise on production line simulator (1)
-

Exercise on production line simulator (2)
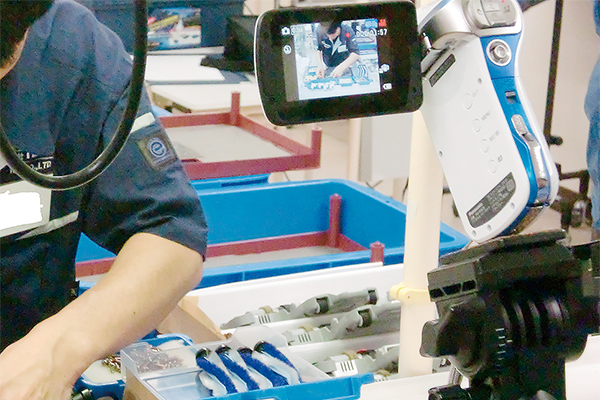
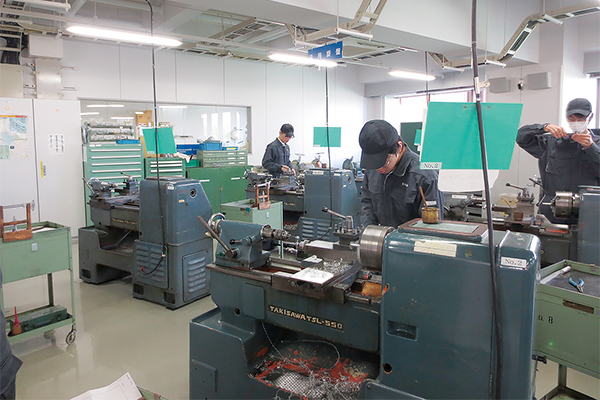
Monodzukuri Center (MONOLAB.)
-

Advanced Practice for Development Process
-
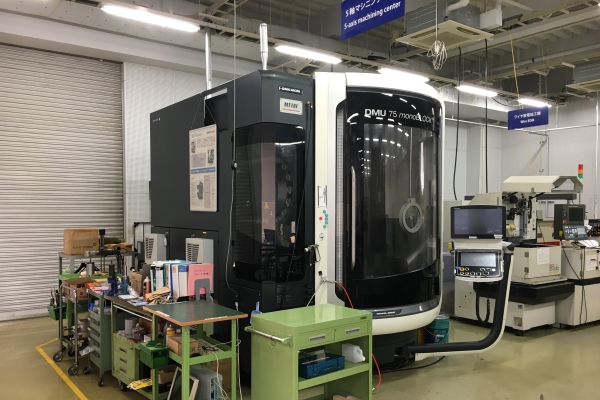

5-axis machining center
Nanomaterials Microdevices Research Center
-
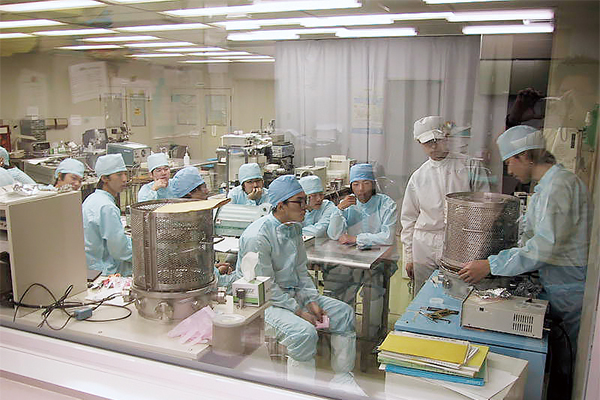

Lab. course for semiconductor device fabrication
-
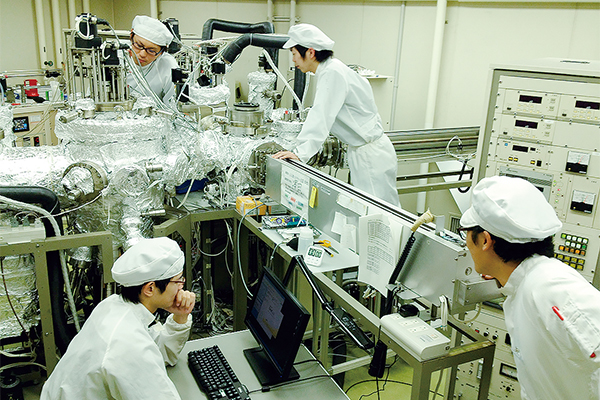

Research for semiconductor thin film fabrication by graduate students.
| Name (LAST NAME, First Name) * Click Name for Details |
Title | Research Field | Related Info. |
| MAEMOTO, Toshihiko | P※ | Semiconductor devices, New functional devices, Oxide semiconductors, Thin-film devices, Flexible devices | |
| WADA, Hideo | P | Applied physics, Electronic and electrical material engineering | Project |
Research Center for Environmental Bioresource
Robotics & Design Center

Xport

Digital Archives Center
-
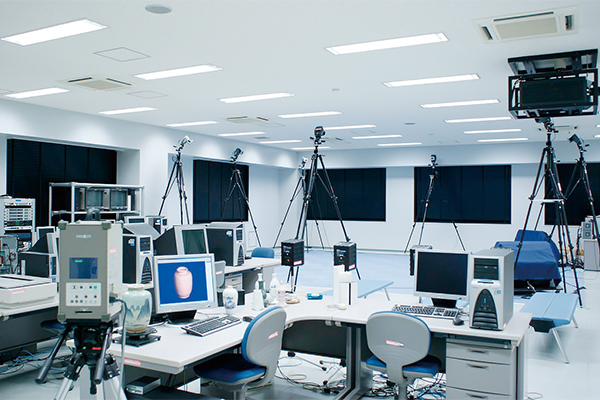

DAC is established to archive digital medias translate from the real world.
-
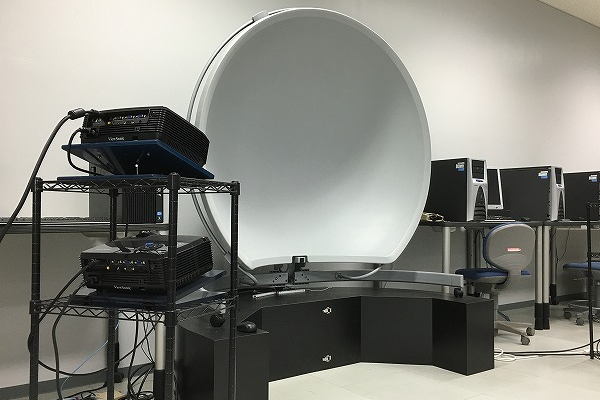

High-brightness spherical screen and multi-projector system
Human Robotics R&D Center
-
Life support type robot
-
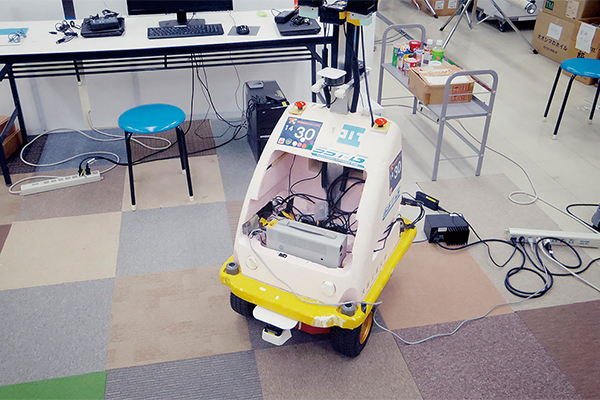

Guide dog robot
Virtual Reality Laboratory
-
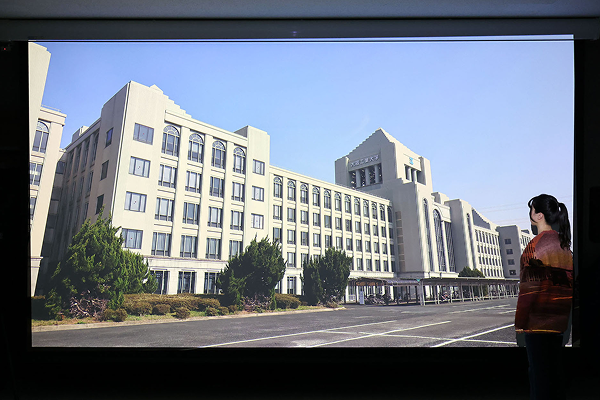

200-inch large-screen 8K video
-
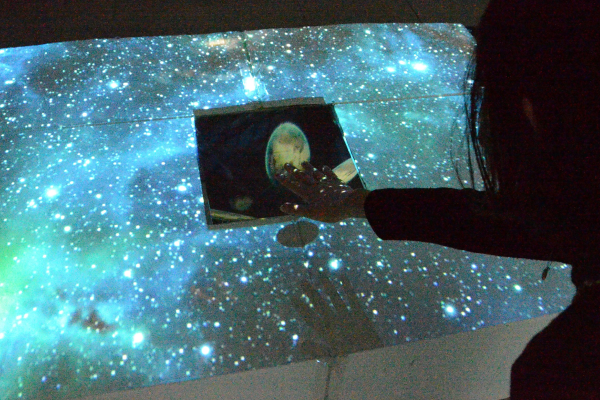

Interactive projection mapping
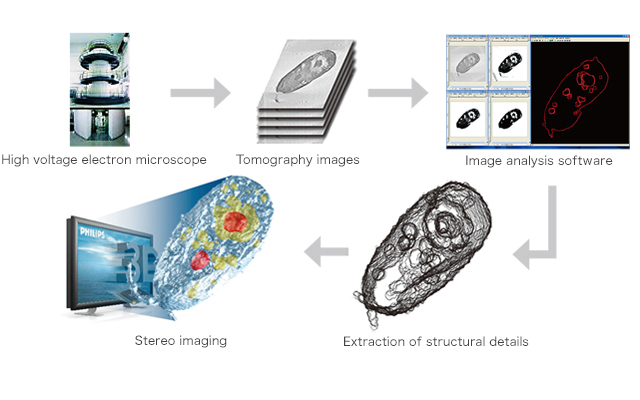
Visualization Software Developing Center
Yawata Engineering Laboratory
Structural Research Center
-
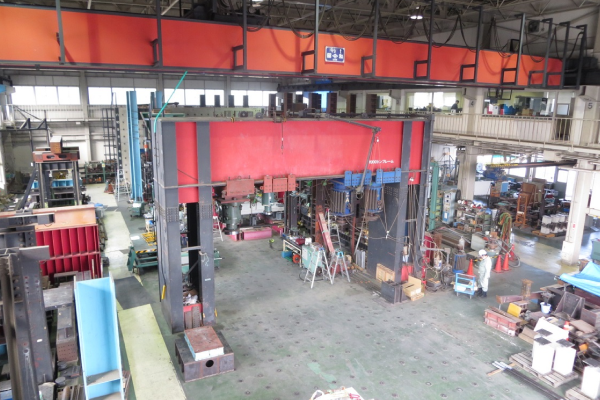

10,000kN Vertical loading equipment
-
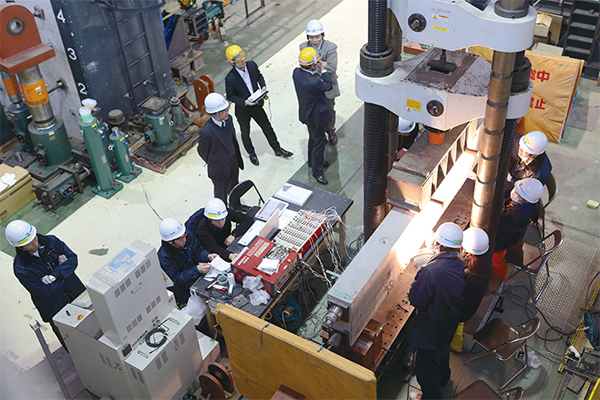

Loading test of prestressed concrete beam
Incubation Lab
| Name (LAST NAME, First Name) * Click Name for Details |
Title | Research Field | Related Info. |
| OCHI, Hiizu | AP | Inorganic materials / Physical properties |






